Thank you for your support at RList Insights all these years!
We are migrating our robotics-related content to apera.io, a platform (beta) which helps you discover companies & products in robotics, AI, IoT, metaverses & other emerging tech. Visit our new home!
An updated 2022 version of this article Autonomous Driving Open Datasets Released To Date (2022) can be viewed at https://apera.io/l/autonomous-driving-open-datasets-release.
We are migrating our robotics-related content to apera.io, a platform (beta) which helps you discover companies & products in robotics, AI, IoT, metaverses & other emerging tech. Visit our new home!
An updated 2022 version of this article Autonomous Driving Open Datasets Released To Date (2022) can be viewed at https://apera.io/l/autonomous-driving-open-datasets-release.
To date, at least 9 large-scale datasets have been released openly to stimulate and accelerate the pace of research into self-driving cars.

Photo of Waymo self-driving car by Grendelkhan
Sources of Dataset
Today, we can already see several autonomous vehicle programs under trial, plying the roads of a number of cites in a controlled environment and collecting critical data for driving in a real-world environment. There are at least 9 well-known large-scale public datasets that researchers can work on for autonomous driving research, from major autonomous driving firms and A.I. research labs.
Waymo Open Dataset, August 2019
Example video of Waymo data collection
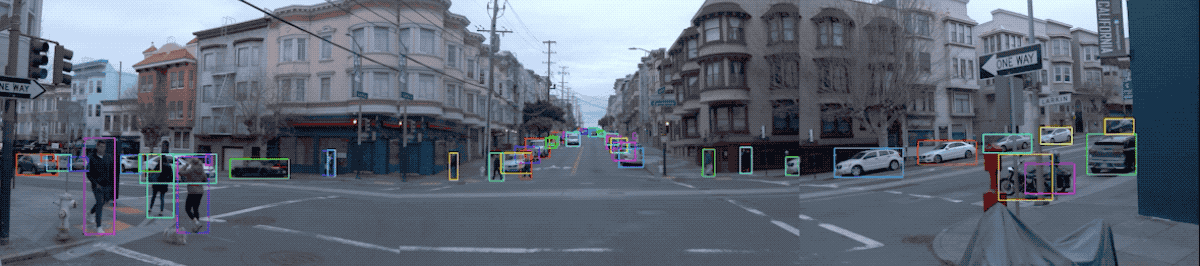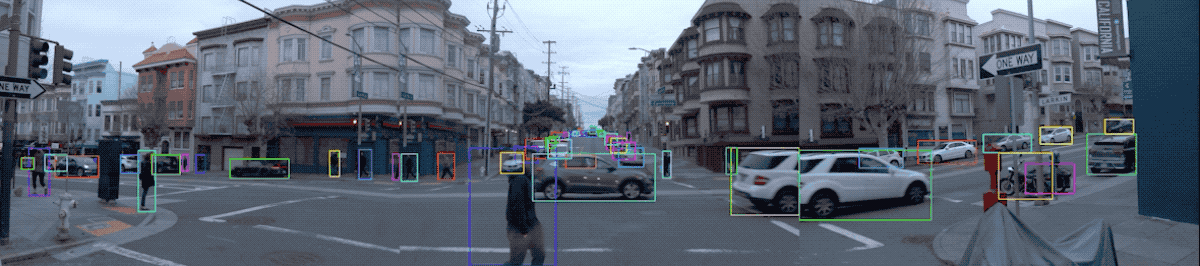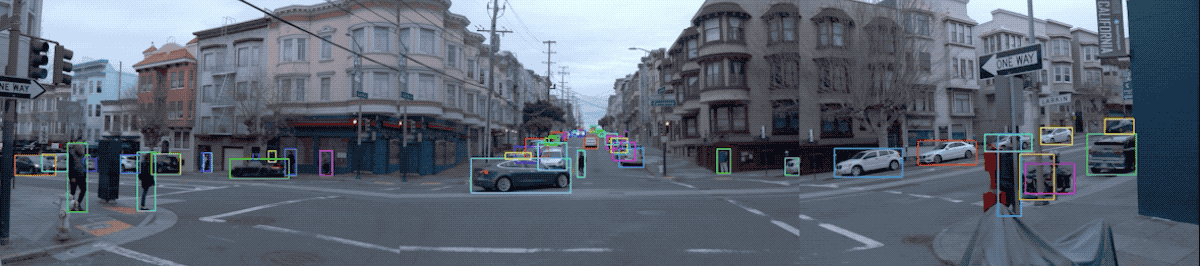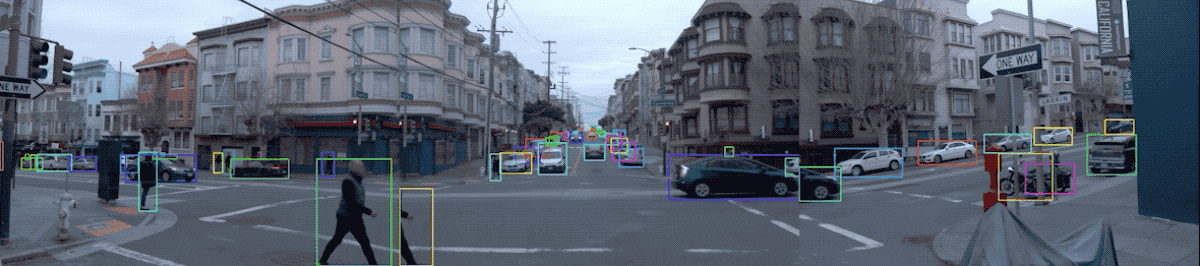
Snapshot of the Waymo Open Dataset (Source: Waymo)
Location/Environment: The dataset covers diverse driving environments, including dense urban and suburban environments across Phoenix, AZ, Kirkland, WA, Mountain View, CA and San Francisco, CA with a wide spectrum of driving conditions (day and night, dawn and dusk, sun and rain).
Lyft Level 5 Dataset, July 2019

Sensor configuration on Lyft's Ford Fusion vehicles for data collection (Source: Lyft)
Location/Environment: San Francisco
Argoverse, June 2019
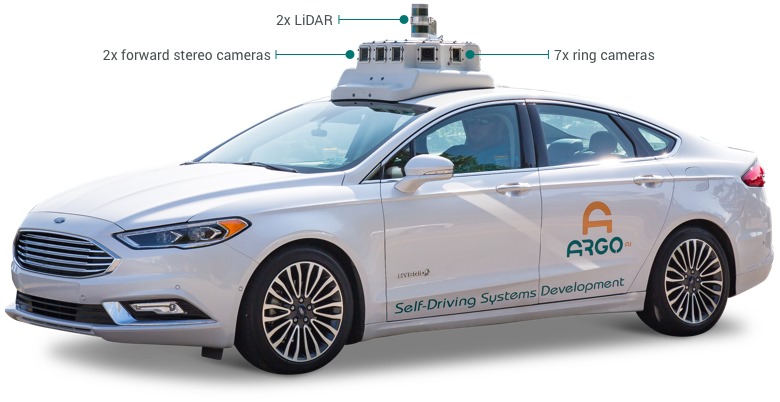
Sensor configuration on Argo's vehicle for data collection (Source: Argo)
According to Argo, the Argoverse Dataset is acquired from cars equipped with 2 roof-mounted LiDAR sensors, 7 HD ring cameras and 2 front-view facing stereo cameras, and includes
- One dataset with 3D tracking annotations for 113 scenes
- One dataset with 327,793 interesting vehicle trajectories extracted from over 1000 driving hours
- Two high-definition (HD) maps with lane centerlines, traffic direction, ground height, and more
- One API to connect the map data with sensor information
Location/Environment: 204 linear kilometers in Miami and 86 linear kilometers in Pittsburgh - two US cities with distinct urban driving challenges and local driving habits, across different seasons, weather conditions, and times of day to provide a broad range of real-world driving scenarios.
Aptiv nuScenes, March 2019
According to Aptiv, the nuScenes Dataset is acquired from the entire sensor suite of an autonomous vehicle (6 cameras, 1 LIDAR, 5 RADAR, GPS, IMU). The entire dataset contains 1,000 scenes of 20 second lengths, which includes approximately 1.4M camera images, 390k LIDAR sweeps, 1.4M RADAR sweeps and 1.4M object bounding boxes in 40k keyframes.
Example video of the nuScene dataset

Sample image from nuScenes (Source: nuscenes.org)
Location/Environment: Boston and Singapore, two cities that are known for dense traffic and highly challenging driving situations.
Berkeley BDD100K, June 2018
Datasets released in 2019 by Aptiv, Argo, Lyft and Waymo have started to incorporate multi-modal data from other sensors such as LiDAR, radar and stereo cameras. BDD100K was released in June 2018 and while it lacks the multi-modal data of its newer counterparts, it is the largest dataset based on monocular videos with 120 million image frames across multiple cities, weather conditions, times of day and scene types.
Comparison between BDD100K and other autonomous driving open datasets released before it (source: https://bair.berkeley.edu/blog/2018/05/30/bdd/)
Baidu ApolloScape, March 2018
The ApolloScape is part of the Baidu Apollo Program. Its dataset contains RGB videos with high-resolution image sequences (146,997 frames) and per-pixel annotation, along with survey-grade dense 3D points with semantic segmentation. The data is collected in different cities under various traffic conditions using mid-sized SUVs equipped with high resolution cameras and a Riegl acquisition system.

Hesai & Scale PandaSet, coming soon
Combining Hesai’s best in class LiDAR sensors with Scale’s high-quality data annotation, the full PandaSet dataset will feature:
- 60,000 camera images
- 20,000 LiDAR sweeps
- 125 scenes of 8s each
- 28 annotation classes
- 37 semantic segmentation labels
- Full sensor suite: 1x mechanical LiDAR, 1x solid-state LiDAR, 6x cameras, On-board GPS/IMU

Sensor configuration on Hesai and Scale'svehicle for data collection (Source: https://scale.com/open-datasets/pandaset)
Location/Environment: Pandaset scenes are selected from 2 routes in Silicon Valley: (1) San Francisco; and (2) El Camino Real from Palo Alto to San Mateo, showcasing complex urban driving scenarios, including steep hills, construction, dense traffic and pedestrians, and a variety of times of day and lighting conditions in the morning, afternoon, dusk and evening.
Where are we today, in terms of autonomous driving?
There are six levels of driving automation in SAE (Society of Automobile Engineers) International's J3016TM driving automation standard from Level 0 (No driving automation) to Level 5 (Full driving automation). Most vehicles on our roads today are at Level 0, that is, manually driven. Tesla Autopilot and Cadillac Super Cruise qualify as Level 2. The 2019 Audi A8L with Traffic Jam Pilot will be classified at Level 3 when rolled out. Level 4 vehicles are in geo-fenced test-bedding stages at the moment and that is the frontline research of autonomous driving in the world today.
A future of Level 5 fully autonomous driving will greatly reduce fatalities on the road, solve traffic issues such as congestion and parking, and improve the environment by reducing personal cars on the road and maximizing shared transport.
Meanwhile, you may also be interested in U.S. states that have legalized PDDs (personal delivery devices or autonomous robots that perform last-mile deliveries within a community) in the past three years, namely, Virginia, Idaho, Wisconsin, Florida, Ohio, Utah, Arizona, Washington, Texas, North Carolina, Missouri, Colorado and Tennessee.
Check out our article on the U.S. States That Have Legalized Personal Delivery Devices (PDDs) Or Last-Mile Autonomous Delivery Robots.




